|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
||

|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
GbE single mode links operate over 1310nm while SONET wavelengths vary over a number of channels defined by the ITU grid. A GbE or SONET design implements the E/O functionality using a standard 9 pin form-factor, SFF (small form factor) or SFP (small form pluggable) module supplied by vendors such as Infineon or Agilent. The use of such a module makes the E/O portion of the design very simple wrt a long haul SONET design in that no driver chip or modulator is required.
After the SERDES device GbE data must be decoded and processed using a MAC device. The decoding is necessary because before transmission the data was coded to help with clock recovery, byte synchronization and to insert inband control codes.
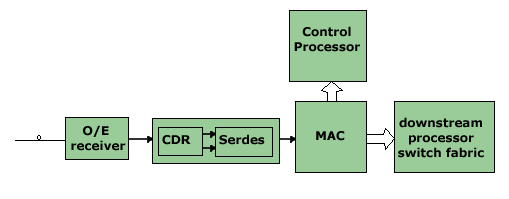
The MAC device could be implemented using a dedicated device, programmable FPGA or integrated into a switching device. The main function is to handle the layer 2 functions of an Ethernet network including address recognition, 8/10b decoding and control code handling. The data stream out of the MAC device can be sent to an embedded processor or to a dedicated switch fabric to handle upper switching functions.